Weight loss surgery entails long term modification in the diet
and lifestyle of patients. This has to be clearly explained to the patients in
the pre-operative counselling sessions so that they have a good compliance
after the surgery which in turn would lead to the desired weight loss goals.
 The post-operative diet is low in calories (carbohydrates
and fats) with high protein. This helps in fat loss without causing loss of
muscle mass which could be harmful for the body. The diet is gradually
progressed from a clear liquid to normal diet over several stages to allow the
person to adjust to the new anatomy and allow the internal organs to heal. A
clear liquid diet is usually started the next day after the surgery which is
continued for 4-5 days.
The post-operative diet is low in calories (carbohydrates
and fats) with high protein. This helps in fat loss without causing loss of
muscle mass which could be harmful for the body. The diet is gradually
progressed from a clear liquid to normal diet over several stages to allow the
person to adjust to the new anatomy and allow the internal organs to heal. A
clear liquid diet is usually started the next day after the surgery which is
continued for 4-5 days.
The patients asked to sip slowly and take only 30-50 ml
at one time to prevent bloating and vomiting. This is then progressed to full
liquid diet containing juices, soups, buttermilk, dal and rice water in the
next week. After 15 days of surgery, a
pureed/soft diet can be given and patients are usually on a normal diet one
month after their procedure.
There are several do’s and don’ts for the patients
Do’s
1. Eat
regularly at proper scheduled time.
2. Meals
should be small and frequent, usually 3-5 meals with two in between snacks
3. Eat food
slowly and chew thoroughly
4. Take
measured portions to avoid overeating
5. Proteins
should be taken at the beginning of the meal
Don’ts
1. High
calorie drinks like shakes, smoothies and sweet juices are a strict no-no
2. Avoid
drinking water during and for 30 minutes before and after your meal
3. Avoid
aerated drinks and using straws as they can cause bloating
4. Avoid
alcohol and smoking
Exercise is an essential part of any weight loss programme
and the same is true of bariatric surgery. Light exercise is started after the
first week of surgery. This includes walking on level ground or working on a
cross trainer/stepper. Resistance exercises are usually recommended after the
first month. Moderate weight training is also helpful to prevent muscle wasting
and loss of bone mass.
Generally, a patient is told to do moderate level
aerobic exercise (i.e. jogging) for 20-30 minutes every day and a total of 300
minutes every week. This also helps maintain healthy skin and muscle tone which
prevents skin sagging which might be experienced by older patients after their
surgery.
There is a need for strict follow up for some time after
your bariatric surgery to ensure that weight loss is according to the plan and
there are no any side effects. We advise follow up visits at 2 weeks, 1 month,
3 months, 6 months and 1 year after the procedure. Thereafter, follow up can
every year by visits or simply telephonic consultations or via e Email.
We check for the following things during the visit
1. Weight
loss- real and expected
2. Diet plan
3. Supplements
4. Blood
tests to detect deficiencies
5. Consultation
for any medical problems
6. Exercise
programme
7. Support
group activities
The weight loss after bariatric surgery is usually in two
phases- initial phase of rapid weight loss which lasts 3-5 months and the
second phase of more gradual weight loss which may continue for 1-2 years
The total expected weight loss is calculated as in terms of
the excess weight which was present before the surgery. 100% of EWL (excess
weight loss) is ideal which means that the person would reach his/her ideal
weight after the procedure. The percentage of excess weight loss varies
according to the procedure and is usually as follows-
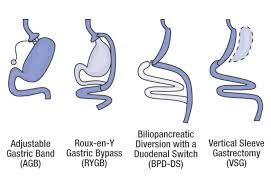
1. Gastric
banding – 50 -60%
2. Laparoscopic
Sleeve gastrectomy – 60- 80%
3. Laparoscopic
Mini gastric bypass – 70- 90%
4. Laparoscopic
Roux en Y gastric bypass – 70 -90%
The
main advantage of bariatric surgery over other weight loss treatments is that
the weight loss has been demonstrated to be sustained over the long term eg.
5-10 years after the procedure. This makes it a permanent solution for obesity.